H-Index in Google Scholar and Scopus: A Comparison


The H-index is a widely used metric that measures the productivity and impact of a researcher's published work. In Google Scholar, the H-index is calculated based on the number of publications and the number of citations those publications have received. It determines the highest number, h, for which a researcher has h publications that have each received at least h citations.

Similarly, Scopus, another popular citation database, also calculates the H-index. Scopus calculates the H-index by considering the number of publications and the number of citations received by those publications. It identifies the highest number, h, for which a researcher has h publications that have each received at least h citations.

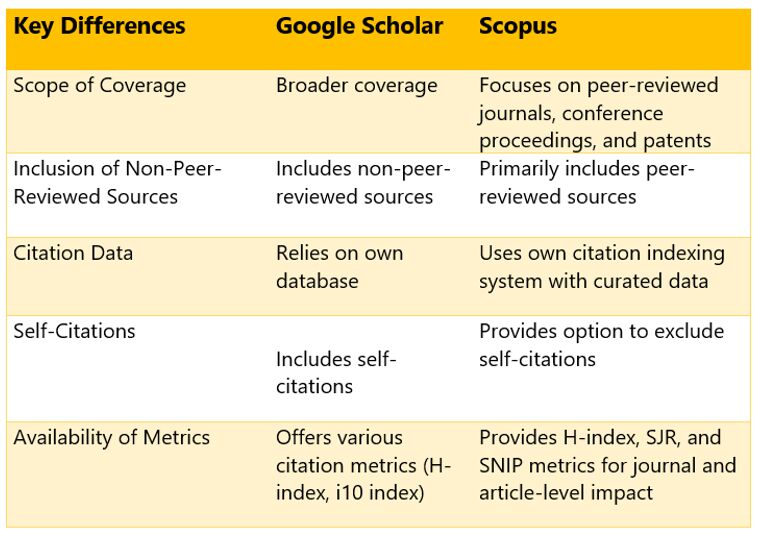
One of the primary differences between Google Scholar and Scopus is the scope of their coverage. Google Scholar has broader coverage, including more comprehensive coverage of scholarly sources such as articles, theses, conference papers, preprints, and institutional repositories. Scopus, on the other hand, focuses specifically on peer-reviewed journals, conference proceedings, and patents.
Google Scholar includes non-peer-reviewed sources in its index, which can lead to a higher number of publications and citations. That can potentially inflate the H-index compared to Scopus, which primarily includes peer-reviewed sources.
Another notable difference is the treatment of self-citations. Google Scholar includes self-citations, meaning citations from a researcher's publications, in the calculation of the H-index. In contrast, Scopus provides an option to exclude self-citations, allowing researchers to assess their impact without self-influence.
The sources of citation data also differ between Google Scholar and Scopus. Google Scholar relies on its database, including citations from various sources, while Scopus uses its citation indexing system. The citation data in Scopus is more curated and reliable as it undergoes rigorous quality control processes.
Google Scholar provides various citation metrics, including the H-index and the i10 index, which represent the number of publications with at least ten citations. Scopus also offers the H-index and additional metrics such as the SJR (SCImago Journal Rank) and SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper) metrics, which provide insights into journal and article-level impact.
When comparing H-index values between Google Scholar and Scopus, it is essential to consider the differences in their coverage, citation sources, and treatment of self-citations. Researchers should keep in mind the following considerations:
The coverage and citation patterns may vary across disciplines, and the choice of the database may depend on the specific field of research. Researchers should consider the dominant sources in their discipline and the availability of those sources in Google Scholar or Scopus.
Institutions or funding agencies may have specific preferences or requirements for using citation databases for research evaluation. Researchers should consult relevant guidelines or policies to ensure compliance with institutional or funder expectations.
If researchers want to compare their H-index over time or with other researchers, it is crucial to maintain consistency in the database used. Switching between Google Scholar and Scopus could lead to variations in H-index values due to differences in coverage and citation sources.
H-index values should be interpreted in the context of the researcher's field, career stage, and citation practices within the discipline. Comparisons should be made cautiously, considering the limitations and nuances associated with citation-based metrics.
SITA Academy

At SITA Academy, we understand the importance of maximizing your research impact and H-Index. That's why we offer comprehensive citation services designed to boost your scholarly profile. Our expert team provides personalized guidance on publishing strategies, targeting reputable journals, and enhancing the visibility of your research. Contact us today to explore how our citation services can elevate your research career.
If you have any questions, inquiries, or would like to learn more about our services, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. Our dedicated team is ready to assist you.